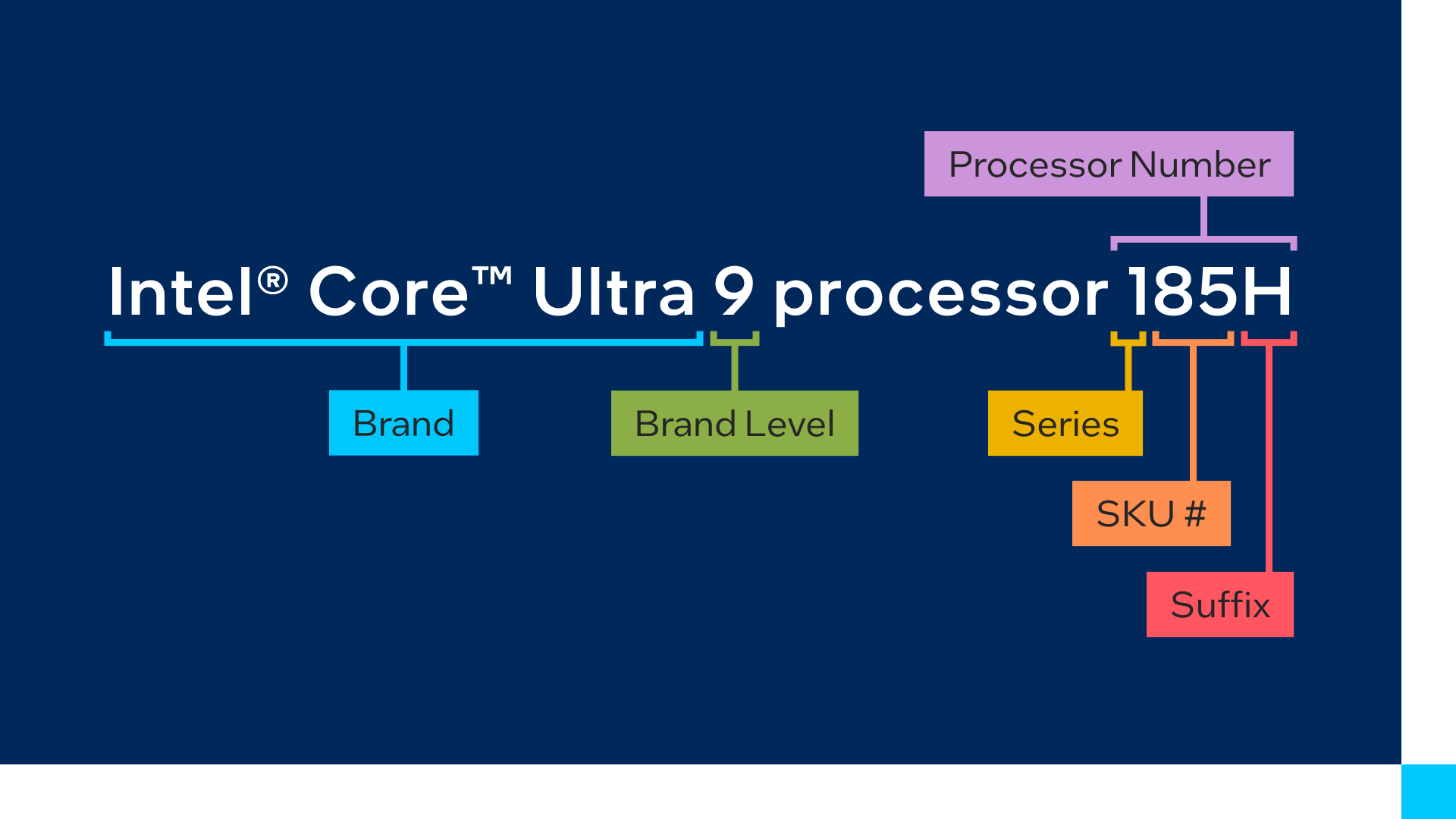
Introduction: Unveiling the Complexities of VirtualDub Appending
VirtualDub, a versatile video capture and processing application, offers users the capability to seamlessly merge or append multiple video files. This article delves into the intricacies of VirtualDub appending, exploring the nuances of its file naming conventions, the challenges involved, and the strategies employed to overcome these obstacles.
File Naming Conventions: A Path of Precision
At the heart of VirtualDub appending lies the task of assigning appropriate file names to the merged videos. The primary approach involves appending a unique identifier to the beginning of the original file name, ensuring that each appended file is easily distinguishable. However, this simplicity can be marred by the presence of file names containing special characters, spaces, or unsupported formats.
Special Characters: Tricky Terrain
Spaces and File Extensions: Obstacles to Avoid
Spaces and unsupported file extensions can also disrupt the file naming process. Spaces must be represented as %20 in the file name, while file extensions must adhere to VirtualDub's supported formats (e.g., .avi, .mp4). Failure to observe these conventions can result in truncated or corrupt appended videos.
Challenges and Strategies: Navigating the Appending Labyrinth
File Size Limitations: Breaking the Barriers
Appending large video files can encounter file size limitations, particularly in older versions of VirtualDub. To overcome these restrictions, users can utilize specialized software, such as Video ReDo or DVD Flick, which support larger file sizes. Alternatively, they can split the original files into smaller segments and append them separately.
Frame Rate Disparities: Harmonizing the Visuals
Differences in frame rates between appended videos can lead to visual inconsistencies. VirtualDub offers the "Assume Frame Rate" option to maintain a consistent frame rate throughout the appended video. However, this may introduce frame drops or duplications, depending on the frame rates of the source files.
Audio Synchronization: Bridging the Gaps
Audio synchronization issues may arise when merging videos with varying audio track lengths. VirtualDub provides the "Input Audio Output Shift" option to manually adjust the audio-video timing. Alternatively, external audio editing software can be used to align the audio tracks before appending.
Scholarly Perspectives and Real-World Applications
Scholarly Insights: Illuminating the Technicalities
Researchers have explored the technical aspects of VirtualDub appending, proposing algorithms and techniques to optimize the process. For instance, a study by Li et al. (2016) presented a novel method for reducing video fragmentation during appending, improving overall performance.
Real-World Applications: Enhancing Video Creation
VirtualDub appending finds practical applications in video editing, surveillance systems, and media archiving. It empowers users to seamlessly merge videos from multiple sources, create time-lapse videos, and archive footage for safekeeping.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Guide to VirtualDub Appending
In conclusion, VirtualDub appending offers a powerful tool for merging video files, but it also necessitates a thorough understanding of its file naming conventions and potential challenges. By addressing these complexities with precision, employing appropriate strategies, and leveraging scholarly research, users can unlock the full potential of VirtualDub appending, enhancing their video editing capabilities and achieving exceptional results.
Linda Black's Horoscope: Will YOUR Zodiac Sign Thrive This Week?
Fanuc Timeout Line Nightmare? This Simple Fix Could Save Your Day!
BMP-24-740: Everything You Need To Know (and More!)

![The Ultimate Jeep Naming Guide [Jeep Names for Every Color] | Off Road](https://149759752.v2.pressablecdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/philippe-toupet-bMgsIepVv_Q-unsplash-1.jpg)