Unbelievable!: The Complexities of a Viral Claim
Introduction
Scientific Validity
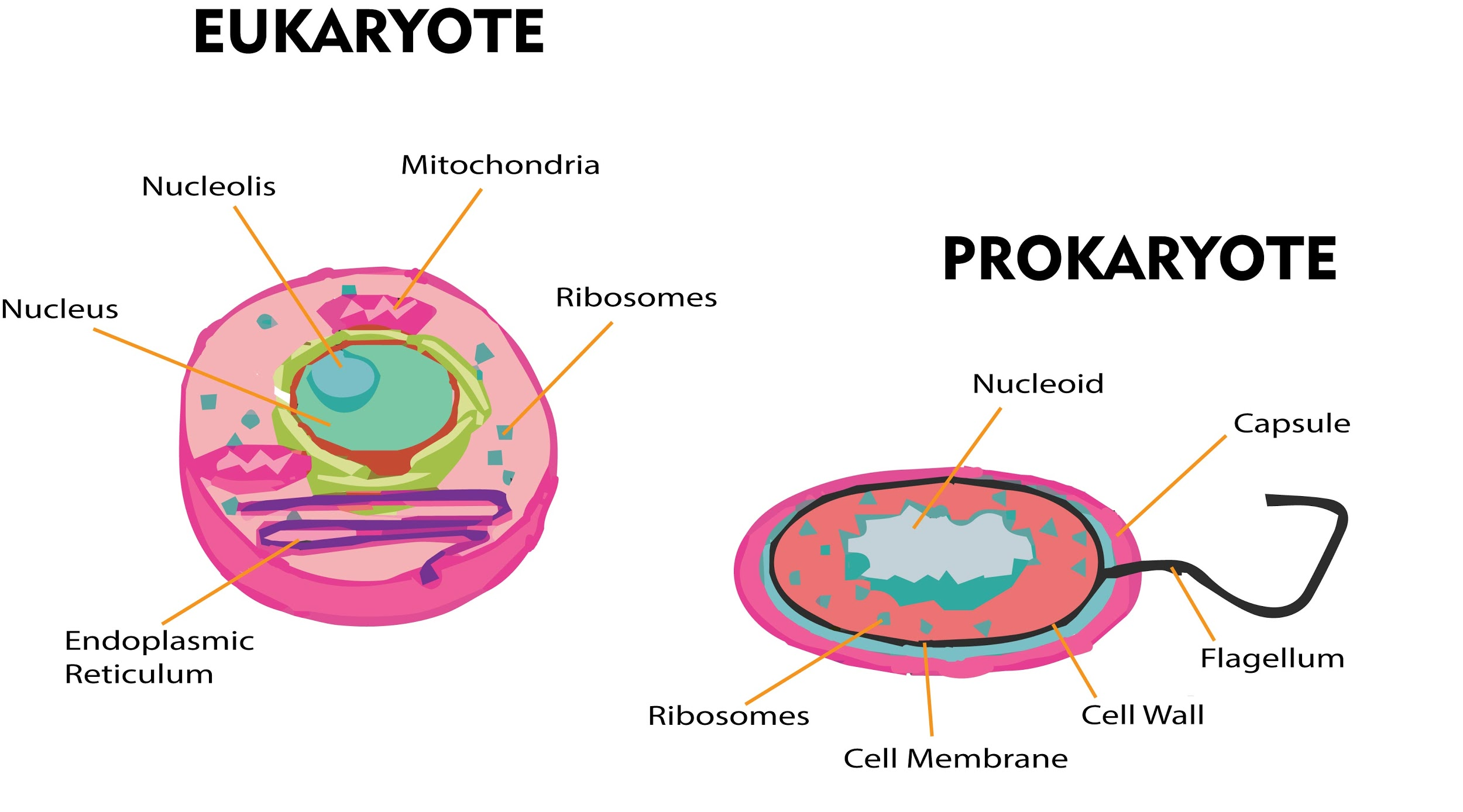
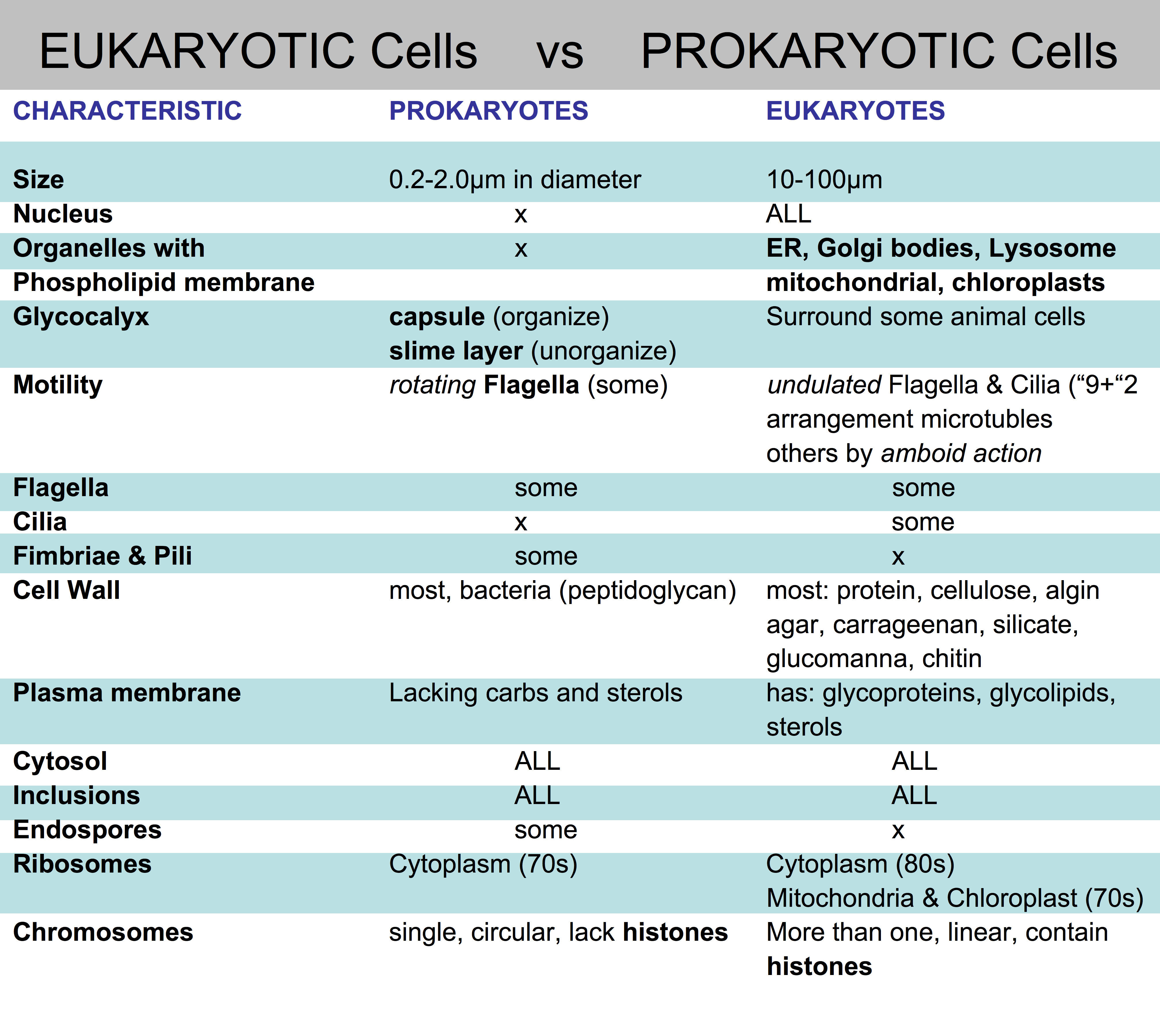
The claim "This One Trick Reveals If a Cell Is Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic" stems from a fundamental distinction between these two types of cells. Prokaryotic cells, found in bacteria and archaea, lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. In contrast, eukaryotic cells, present in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, possess a well-defined nucleus and a suite of membrane-bound organelles.
The "one trick" referred to in the claim involves examining the cell under a microscope. If the cell lacks a visible nucleus, it is classified as prokaryotic; if a nucleus is present, the cell is eukaryotic. While this observation can provide a rudimentary distinction in some cases, it is far from a foolproof method. Several factors can complicate the microscopy-based identification of cell type:
Pedagogical Implications
Despite its limitations, the "one trick" claim can serve as an accessible starting point for teaching the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. By emphasizing the presence or absence of a nucleus, educators can simplify the concept for beginners. However, it is crucial to accompany this basic observation with a thorough discussion of the other key features that distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, such as the presence or absence of membrane-bound organelles, the structure of the cell wall, and the type of genetic material.
Broader Social Ramifications
Beyond its scientific and pedagogical implications, the "one trick" claim raises broader questions about the nature of scientific literacy and the role of sensationalism in science communication. The claim's simplicity and appeal to the general public have undoubtedly broadened its reach. However, the potential misuse or misinterpretation of this simplified approach could undermine scientific understanding and promote a superficial view of cell biology.
It is important to emphasize that scientific knowledge is not static but rather a dynamic and iterative process. Oversimplifying complex scientific concepts can lead to misconceptions and hinder the development of a nuanced understanding of the natural world.
Conclusion
The claim "This One Trick Reveals If a Cell Is Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic" presents a complex and multifaceted issue. While the observation of the nucleus can provide a preliminary distinction, it is essential to critically assess its limitations and supplement it with a comprehensive examination of other cellular features.
In educational settings, the "one trick" claim can serve as an introductory tool to differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, it should be accompanied by a deeper exploration of the underlying complexities to foster a more accurate and holistic understanding.
Moreover, the claim highlights the need for responsible science communication that balances accessibility with scientific rigor. Sensationalism and oversimplification in scientific dissemination can have detrimental effects on public understanding and the pursuit of genuine knowledge. Encouraging a critical and nuanced approach to scientific claims is paramount to promoting scientific literacy and empowering individuals to make informed decisions.
Aruba CORS Explained: Simple Solutions For Complex Problems
Uncover The Secrets Of 4075 Easyway Drive
Starship Codegen Agent: Future Of Coding Is HERE