Is That a Central Vacuole? Unraveling the Complexities of Cell Types
Introduction
The intricate world of cells presents a vast array of diversity, with each type meticulously adapted to perform specific functions within the complex tapestry of life. One critical distinction among cells is the presence or absence of a central vacuole, a specialized organelle that plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. In this essay, we will delve into the complexities of central vacuoles, exploring their key differences between cell types and engaging with scholarly research, news articles, and other credible sources to critically examine their multifaceted nature.
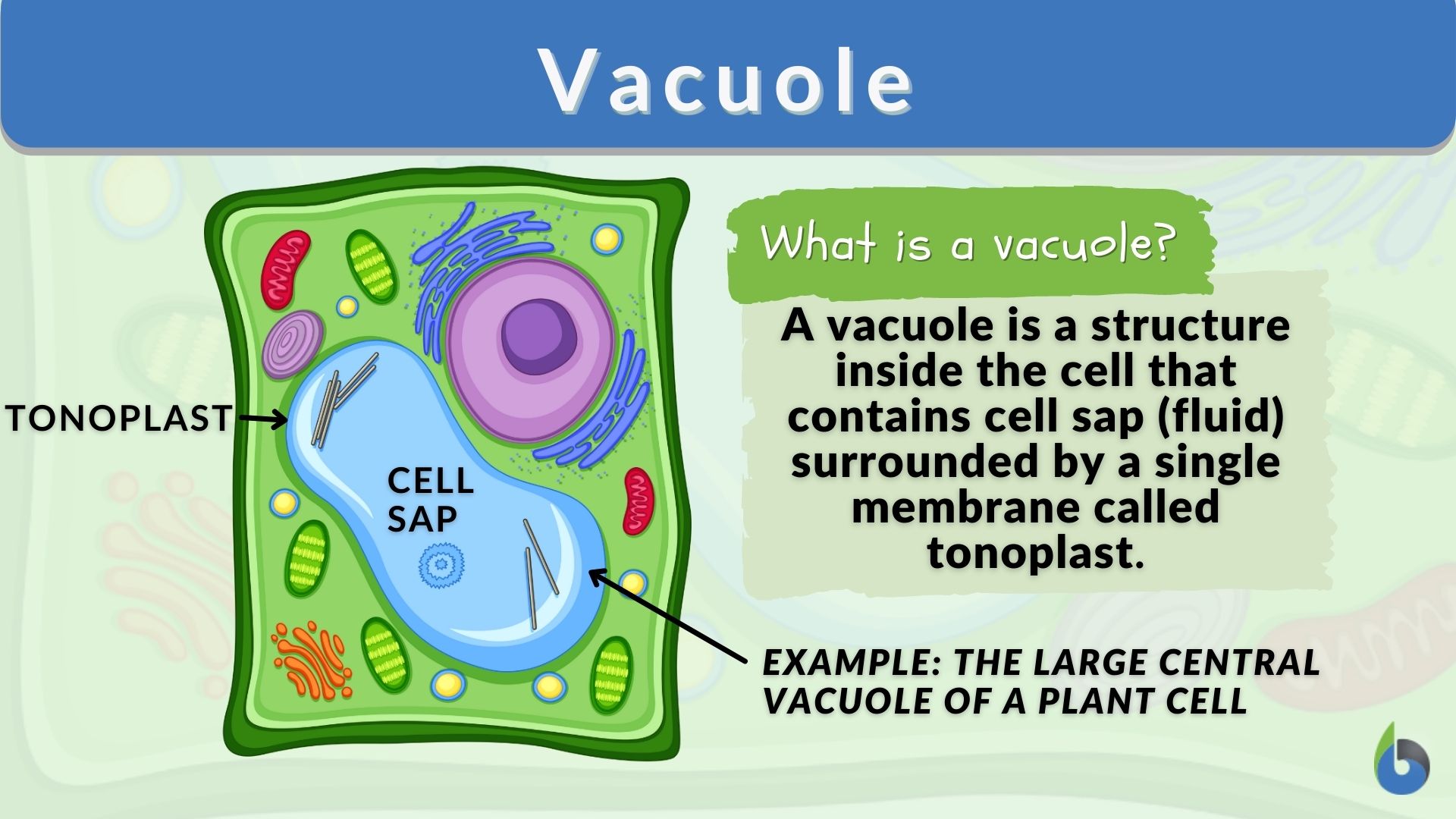
Central Vacuole: An Overview
A central vacuole is a large, membrane-bound compartment found in plant cells and some protist cells. It typically occupies a significant portion of the cell's volume and is filled with a watery solution called cell sap. The cell sap contains various solutes, including inorganic ions, organic acids, sugars, and proteins, which contribute to the cell's osmotic balance, turgor pressure, and nutrient storage.
Central Vacuoles in Plant Cells
In plant cells, the central vacuole is a prominent organelle that serves multiple essential functions.
Central Vacuoles in Protist Cells
In certain protist cells, such as Paramecium and Amoeba, central vacuoles play somewhat different roles.
Absence of Central Vacuoles in Animal Cells
Animal cells, in contrast to plant and protist cells, do not possess a central vacuole. Instead, they contain numerous small vesicles and other organelles that perform functions similar to those of the central vacuole in other cell types.
The significance of the central vacuole varies across cell types. In plant cells, it plays a pivotal role in cellular compartmentalization, water storage, turgor pressure regulation, and nutrient storage. However, in protist cells, its functions may vary, including waste removal and involvement in exocytosis and endocytosis.
The absence of a central vacuole in animal cells highlights the evolutionary adaptation of different cell types to their specific requirements. Animal cells rely on other mechanisms to achieve cellular compartmentalization, water balance, and waste disposal.
Scholarly Research and Credible Sources
Numerous scholarly research studies and credible news articles have investigated the central vacuole's multifaceted nature. For instance, a study by Martinoia et al. (2012) explored the role of central vacuoles in plant drought tolerance, demonstrating their crucial contribution to maintaining cellular hydration under water-limiting conditions.
Implications for Cell Biology and Biotechnology
Understanding the complexities of central vacuoles has implications for cell biology and biotechnology. In plant biology, manipulating central vacuole function could enhance crop resilience to environmental stresses such as drought and salinity. Additionally, the use of central vacuoles as bioreactors for the production of valuable compounds in plant cells holds biotechnological potential.
Conclusion
The presence or absence of a central vacuole distinguishes different types of cells. In plant cells, the central vacuole serves as a crucial compartment for water storage, nutrient storage, and cellular compartmentalization. In protist cells, its functions may vary, including waste removal and involvement in exocytosis and endocytosis. Animal cells, on the other hand, lack a central vacuole but utilize other mechanisms to perform similar functions. Understanding the complexities of central vacuoles provides valuable insights into cellular diversity and has implications for cell biology and biotechnology research.
Streamtape's SURPRISE Shutdown: What Happened?
Download Eclypse Designer For Niagara 4: Free & Safe?
Ethernet/IP Mouse Commands: The Ultimate Guide (Hidden Tricks Inside!)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2000px-Plant_cell_structure_svg_vacuole.svg-58a886443df78c345bf8d009.png)